Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction
Breast reconstruction with implants is the most common method of reconstruction. Implants available today are very safe and can produce a beautiful and youthful result.

what is implant-based Breast Reconstruction?
The most common method of breast reconstruction in the United States uses implants to recreate the breast. Smooth-walled silicone gel implants are the most frequently used and are very safe. They have a soft and natural feel, and can create a beautiful and youthful breast shape.


Benefits of Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction
- Youthful and attractive result
- Excellent symmetry when bilateral mastectomies and reconstructions are performed
- Less extensive operation
- Shorter hospitalization
- Generally easier recovery
- Tissue expanders allow patients to choose their ultimate size

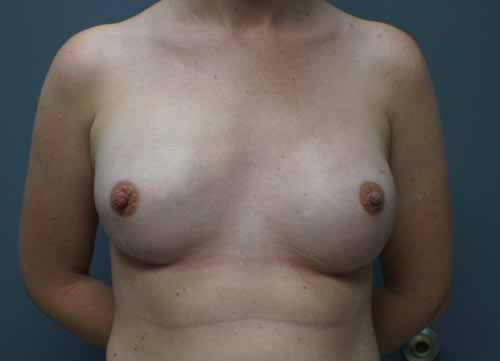
Bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and direct to implant reconstruction.
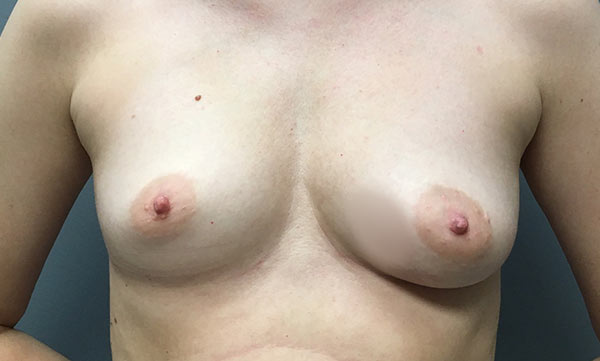
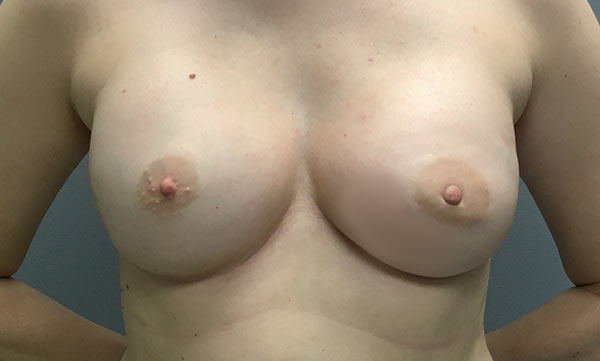
Bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomies and tissue expander to implant reconstruction
Who Is A Candidate?
Most women are candidates for implant-based reconstruction. In cases where a portion of the breast skin is removed, a tissue expander can be used to stretch the remaining skin in preparation for an implant. If the breast skin and nipple are preserved, an implant can sometimes be placed at the time of the mastectomy. The best candidate for a direct-to-implant reconstruction has smaller breasts and healthy skin following the mastectomy.
Women undergoing bilateral mastectomies are usually great candidates for an implant-based reconstruction, as good symmetry can be achieved.
A successful implant-based reconstruction requires a healthy skin envelope. Prior radiation to the breast can damage the skin and impact its ability to heal and expand. When the radiation injury is severe, an autologous reconstruction may be a better option. Some women require radiation after their mastectomy. While most women can successfully complete tissue expansion and placement of an implant, the risk of complications is higher.
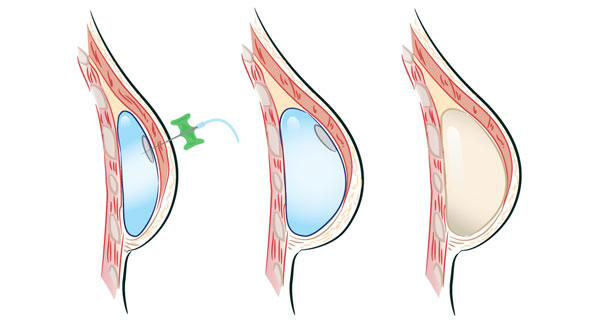
Profile view of breast with tissue expander in place. A needle is inserted through the skin into a magnetized port to fill the expander. Fully inflated tissue expander. A corresponding implant ultimately replaces the tissue expander.
Implant-Based Reconstruction: What To Expect
- The first stage of reconstruction can usually be performed at the time of the mastectomy.
- If there is insufficient breast skin or the woman desires a larger breast, a temporary tissue expander can be placed to gradually expand the breast to the size desired.
- A one-sided tissue expander or implant reconstruction takes approximately 1 to 2 hours.
- Patients generally stay in the hospital overnight, but a complete recovery may take 3-4 weeks.
- If a tissue expander was placed at the first surgery, the process of expansion in the office usually begins 3 or 4 weeks later.
- Most women undergo expansions every 2 weeks. Depending on the size breast desired, the process can take weeks or months.
- After expansion is complete, surgery to replace the tissue expander with an implant is usually performed about one month later. Some refinements to the reconstruction, like fat transfer, can also be done at this stage.
- Subsequent operations are often planned to refine the reconstructed breast, create a nipple, or to balance the opposite side.
During your consultation, share your goals and priorities with Dr. Davison and Dr. Pinell. This will help them identify the best method of reconstruction for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Can breast reconstruction be performed at the time of the mastectomy?
In many cases, yes. Immediate breast reconstruction is generally safe, produces the best aesthetic result, and is beneficial to coping with the loss of a breast.
-
What are the risks of an implant-based breast reconstruction?
As with any operation, bleeding, infection, fluid pockets, and problems of wound healing can occur.
Complications related to the implant include malposition of the device, rippling, rupture or leak, infection, and capsular contracture—dense scarring around the implant that can distort the breast shape or be uncomfortable.
-
How long does reconstruction with an implant or tissue expander take, and how long is a patient usually in the hospital?
A unilateral (one-sided) implant reconstruction takes 1 to 2 hours. Patients are generally hospitalized overnight.
-
What is the recovery time following reconstruction with an implant or tissue expander?
Patients should be out of bed the day after surgery and then gradually increase their activities from that point forward. While most women have resumed a modified daily routine by 2 weeks, a full recovery can take 3 to 4 weeks.
-
Can a permanent breast implant be placed at the time of the mastectomy?
Most women benefit from a 2-stage reconstruction, where a tissue expander is placed at the time of the mastectomy and later replaced with a permanent implant. A tissue expander is used to replace skin that is removed with the mastectomy or to replace skin that is removed with the mastectomy or to stretch the skin to accommodate a larger implant if a woman chooses.
When the breast skin and nipple are preserved by the mastectomy, a breast implant can sometimes be placed at the initial operation. This approach is most successful when reconstructing smaller breasts.
-
Are subsequent surgeries needed after reconstruction with an implant?
Oftentimes, yes. Women will frequently undergo revision procedures to refine or enhance the appearance of the reconstructed breast. Fat transfer is often performed to smooth the contours of the implant. Nipple reconstruction and balancing operations on the opposite breast can be performed at that time as well.
-
Are breast implants safe?
Breast implants carry certain risks—like internal scarring, malposition, and rupture, but they do not increase the risk of breast cancer or autoimmune illness.
A rare type of lymphoma called Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL) has been associated with implants that have a textured surface. In most cases, BIA-ALCL can be cured by removing the textured implant and surrounding scar capsule. Though rare and usually treatable, this condition can be avoided by using a smooth-walled implant, as is the practice at DAVinci Plastic Surgery.
-
Do breast implants last forever?
Breast implants are not lifetime devices, but the current generation of implants do not have a set lifespan or expiration date. Between one-quarter and one-half of women reconstructed with breast implants will undergo a subsequent operation, most commonly to address internal scarring (capsular contracture) or aesthetic concerns.
-
Does insurance cover breast reconstruction with implants?
Yes. All methods of breast reconstruction after a mastectomy and balancing procedures to the opposite breast are generally covered by insurance.
